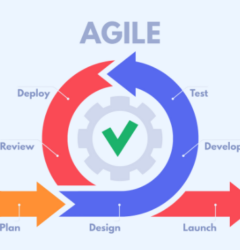
The gap between business demands and IT capacity has never been wider. As organizations race to innovate, traditional development cycles often struggle to keep up with the urgent need for digital solutions. Enter the citizen developer — a game-changing force reshaping how businesses build, automate, and optimize processes.
Citizen developers are not professional coders. They’re business users — HR managers, finance analysts, operations specialists — who deeply understand day-to-day challenges and are closest to the problems that need solving. Armed with intuitive no-code and low-code platforms like Quixy, they can design and deploy applications without writing a single line of code.
Citizen Developers are breaking down barriers and bringing their ideas to life using low-code and no-code platforms.
This shift is more than just a workaround for IT bottlenecks. It represents a new era of business-led innovation, where employees across departments actively contribute to digital transformation. By empowering citizen developers, organizations achieve faster time-to-value, reduce reliance on overburdened IT teams, and create a culture of continuous improvement and ownership.
In the following sections, we’ll explore what a citizen developer is, how they differ from professional developers, and why the citizen development movement is quickly becoming a cornerstone of modern enterprise strategy.
What is a Citizen Developer?
A citizen developer is a non-IT professional who creates apps or automates business processes using IT-sanctioned tools, typically no-code or low-code platforms. In simple terms, citizen developers are employees from functions like HR, finance, marketing, or operations who deeply understand their business challenges and use visual development tools to solve them — without writing traditional code.
The meaning of a citizen developer goes beyond simply building apps; it’s about democratizing innovation and empowering teams to address bottlenecks independently. By bridging the gap between business needs and technical delivery, citizen developers accelerate digital transformation and relieve pressure on overburdened IT departments.

Citizen Developers vs Professional Developers
While both citizen developers and professional developers contribute to digital initiatives, their roles, skills, and approaches differ significantly.
Professional developers are trained software engineers skilled in writing complex code, designing system architectures, and managing large-scale technical projects. They handle mission-critical, enterprise-grade applications that require advanced security, integrations, and scalability.
On the other hand, citizen developers are domain experts who leverage intuitive, drag-and-drop interfaces to build business apps quickly and flexibly. Their focus is on solving specific departmental problems, automating repetitive tasks, or digitizing manual processes.
Instead of replacing professional developers, citizen developers complement them. By handling less complex, internal-facing apps, citizen developers free up IT resources to focus on strategic and high-priority projects. This collaboration fosters a more agile and responsive organization — a key driver for businesses adopting no-code and low-code platforms like Quixy.
Despite their differences, citizen developers and professional developers often collaborate. Citizen developers can quickly prototype ideas and address immediate business needs, while professional developers refine and scale those solutions for broader use. This partnership allows organizations to innovate efficiently while maintaining robust, secure, and scalable systems. Together, these two groups play complementary roles in driving digital transformation and meeting the diverse needs of modern businesses.
Also read: Citizen Developer vs. Professional Developer
Citizen Developmer Movement
The citizen developer movement is more than a technology trend; it’s a strategic evolution driven by the need for speed, flexibility, and continuous innovation. As global markets become more competitive and customer expectations rise, companies can no longer afford to let IT backlogs delay business-critical improvements.
According to Gartner, by 2026, at least 80% of technology products and services will be built by non-IT professionals, reflecting a massive shift toward democratized development. Also, Forrester reports that over 60% of organizations are already either implementing or planning citizen development initiatives to address application backlogs and empower business teams.
As global markets become more competitive and customer expectations rise, companies can no longer afford to let IT backlogs delay business-critical improvements. By embracing citizen development, organizations build a more engaged, tech-savvy workforce that contributes directly to growth and operational efficiency. Tools like Quixy’s no-code platform enable this movement by providing a secure, governed environment where citizen developers can experiment, innovate, and deliver value safely and quickly.
Watch Webinar: The Rise of Citizen Development in Enterprise App Development
Why There is a Rise of the Citizen Developers
This rising CD trend empowers non-technical individuals to become drivers of innovation, propelling digital transformation initiatives to new heights. Let’s see the reasons behind the surge in citizen development and its transformative impact on organizations worldwide.
The momentum behind citizen development is undeniable. According to Gartner, by 2026, 80% of technology products and services will be built by non-IT professionals, signaling a seismic shift in how solutions are created and delivered. The growing accessibility of citizen developer platforms — particularly no-code and low-code solutions — has been central to this rise.
The global market for low-code and no-code platforms supporting citizen development is also booming. According to MarketsandMarkets, this market is expected to reach $45.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of over 20%. This explosive growth highlights how companies are investing in empowering their business users to drive innovation from the ground up.
1. Increasing Demand for Customization and Agility
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations require agile and customized solutions to stay competitive. Citizen development offers a way to rapidly develop applications tailored to specific business needs without relying solely on IT departments. This flexibility and speed have fueled the rise of citizen development.
2. Democratizing Innovation
Citizen development empowers individuals from various departments to actively contribute to innovation. Business users can use no-code or low-code platforms to translate their domain expertise into practical solutions. This democratization of development enables organizations to tap into a broader pool of creativity and problem-solving abilities.
3. Bridging the IT Gap
As the demand for new applications continues to surge, traditional software development processes often find it challenging to keep pace with the requirements. Citizen development bridges the gap by enabling non-technical individuals to create and deploy applications independently. This relieves the burden on IT departments, reduces backlogs, and allows for more efficient resource allocation.
Also Read:Strategy for Problem-Solving Culture with Citizen Development
4. Empowering Business Users
With no-code and low-code platforms becoming increasingly user-friendly, citizen development has become accessible to business users without extensive coding knowledge. This empowerment enhances job satisfaction and encourages a culture of innovation and ownership among employees.
5. Accelerating Digital Transformation
As organizations embrace digital transformation, citizen development is vital in driving change. Organizations can rapidly deploy digital solutions, streamline processes, and adapt to evolving market demands by enabling business users to contribute directly to application development.
Also read: The Pros and Cons of Citizen Development
The Role of Citizen App Developers
Citizen developers don’t just build simple apps; they are creating real business value. As citizen app developers, they develop tools that automate manual tasks, digitize workflows, streamline approvals, and close process gaps that have historically slowed down organizations.
These app creators understand the nuances of their business areas better than anyone else. Whether it’s a procurement manager automating purchase approvals, or an HR specialist digitizing onboarding processes, citizen app developers directly address pain points that traditional IT might not prioritize.
Moreover, citizen app developers play a crucial role in creating a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. By enabling employees to become active problem-solvers rather than passive requesters, organizations become more agile, resilient, and competitive.
Platforms like Quixy make this possible by offering secure, governed environments that allow citizen app developers to build confidently — ensuring compliance, data integrity, and scalability without sacrificing speed.
Benefits and Challenges of Citizen Development
With shortage of IT professionals and large backlogs in IT departments, traditional software development is unable to fulfill the growing need for solutions. Citizen development is transforming how organizations approach digital transformation and process automation. While the advantages are significant, this approach also introduces new challenges that leaders must address to maximize success and minimize risks.
Benefits for Business and IT Teams
1️⃣ Accelerated Innovation and Delivery
Citizen development empowers business teams to build solutions rapidly, reducing reliance on overloaded IT departments. By leveraging intuitive no-code and low-code platforms, employees can develop and deploy applications in days or weeks instead of waiting months for traditional development cycles. This speed is critical in fast-changing markets where adaptability determines competitiveness.
2️⃣ Closer Alignment with Business Needs
Business users — the citizen developers — are closest to operational challenges. Their first-hand insights ensure the solutions they create are practical, relevant, and tailored to actual pain points. This reduces the gap between IT capabilities and business expectations, leading to higher user adoption and satisfaction.
3️⃣ Relief for IT Teams
By enabling business users to handle non-critical, departmental-level app development, IT teams can focus on more strategic, enterprise-scale projects. This approach helps reduce application backlogs, enhances IT productivity, and ensures better resource allocation.
4️⃣ Cost Efficiency
Citizen development minimizes external development costs and reduces the time spent on traditional custom coding projects. Organizations can achieve more with less, improving ROI on digital transformation initiatives.
5️⃣ Fostering a Culture of Innovation
Empowering employees to solve their own problems encourages a culture of ownership, creativity, and continuous improvement. It transforms employees from passive technology users into proactive innovators, boosting morale and engagement across the organization.
“A spectrum of citizen developer roles is emerging. These new roles may not replace traditional software developers, but they can enhance your software delivery strategy by giving your business people the tools they need to innovate on their own.”
John R. Rymer, Vice President, Principal Analyst serving Application Development & Delivery professionals at Forrester
Challenges and Risks: Governance & Control
Despite its many benefits, citizen development also introduces governance challenges that organizations cannot afford to overlook.
Without proper citizen developer governance, there’s a risk of creating “shadow IT” — applications developed and used outside of official IT oversight. This can lead to issues with data security, regulatory compliance, integration errors, and inconsistent user experiences.
Key risks include:
- Security vulnerabilities: Unauthorized or poorly designed apps may expose sensitive data or create security gaps.
- Compliance challenges: Applications built without following corporate or industry standards can lead to regulatory violations.
- Integration conflicts: Apps created by citizen developers may not always align with existing enterprise systems, causing operational silos or data inconsistencies.
- Quality and scalability concerns: Rapidly built apps may lack robust testing and long-term maintenance plans.
To mitigate these risks, organizations need a strong citizen developer governance framework. This includes clear guidelines, pre-approved development tools like Quixy, training programs, and IT support for monitoring and validation. By establishing a balance between freedom and control, businesses can safely scale citizen development initiatives while maintaining data integrity and compliance standards.
Also watch:
Citizen Developer Platforms & Tools
The rise of citizen developers wouldn’t be possible without powerful, user-friendly platforms and tools. These solutions give business users the ability to turn ideas into functional applications without deep technical skills, all while maintaining IT oversight and governance.
Choosing the Right Citizen Developer Platform
Selecting the right citizen developer platform is critical to ensuring successful adoption and long-term scalability. The market for citizen developer platforms has grown rapidly in recent years; in fact, according to Gartner, by 2025, 70% of new applications developed by enterprises will use low-code or no-code technologies.
A robust citizen developer platform should offer:
- Ease of use: A truly intuitive, drag-and-drop interface so business users can build apps without technical barriers.
- Governance and security: Built-in compliance controls, permission management, and IT visibility to prevent shadow IT risks.
- Integration capabilities: Seamless connectivity with existing enterprise systems and third-party applications.
- Scalability: Support for expanding app usage across different teams or departments as needs grow.
Platforms like Quixy empower organizations to support business-led innovation safely and effectively, giving both IT and business leaders the confidence to scale citizen development initiatives.
Popular Citizen Developer Tools & Solutions
Today’s market offers a variety of citizen developer tools, ranging from no-code to low-code solutions, designed to support different business needs and skill levels.
No-code citizen developer tools are ideal for business users who want to create apps entirely visually, without writing any code. They’re perfect for digitizing forms, automating workflows, and building departmental apps quickly.
Low-code citizen developer tools, on the other hand, offer more customization and flexibility. They allow limited coding for more advanced features, making them suitable for more complex use cases where deeper logic or integrations are needed.
These tools play a critical role in low-code no-code citizen developer enablement, helping organizations bridge skill gaps, accelerate digital transformation, and empower employees at all levels to innovate.
When evaluating citizen developer tools, it’s important to consider not only technical capabilities but also user training, vendor support, and the ability to enforce governance standards across the organization.
Low-Code vs No-Code Citizen Developers
While the terms “low-code” and “no-code” are often used interchangeably, they represent two distinct approaches to citizen development.
- No-code citizen developers are typically business professionals with no technical background who use visual builders to create applications. They focus on solving operational challenges quickly, such as automating approvals or digitizing manual workflows.
- Low-code citizen developers may have some technical aptitude or coding familiarity, allowing them to create more complex and customized applications. They can add advanced logic, integrate deeply with enterprise systems, and handle sophisticated use cases.
The choice between low-code and no-code depends on an organization’s specific goals, user skills, and application complexity. Many enterprises opt for platforms that support both approaches, enabling a hybrid strategy where no-code solutions empower broader teams, and low-code capabilities address more specialized needs.
Ultimately, both low-code and no-code citizen developers play a crucial role in accelerating innovation, reducing time-to-market, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement across the organization.
How do No-Code Citizen Development Platforms Work?
Citizen developers start creating their apps using a toolbox that is at their disposal. They simply have to drag and drop visual boxes to add and arrange functionalities and design workflows. Drop-down menus and a colour palette help to provide choice from a set of options, as well as customize or brand the app. What’s more, many citizen development platforms offer ready-made templates for typical business use cases. Citizen developers can employ the template to build additional functionalities on it that are specific to their company’s needs.
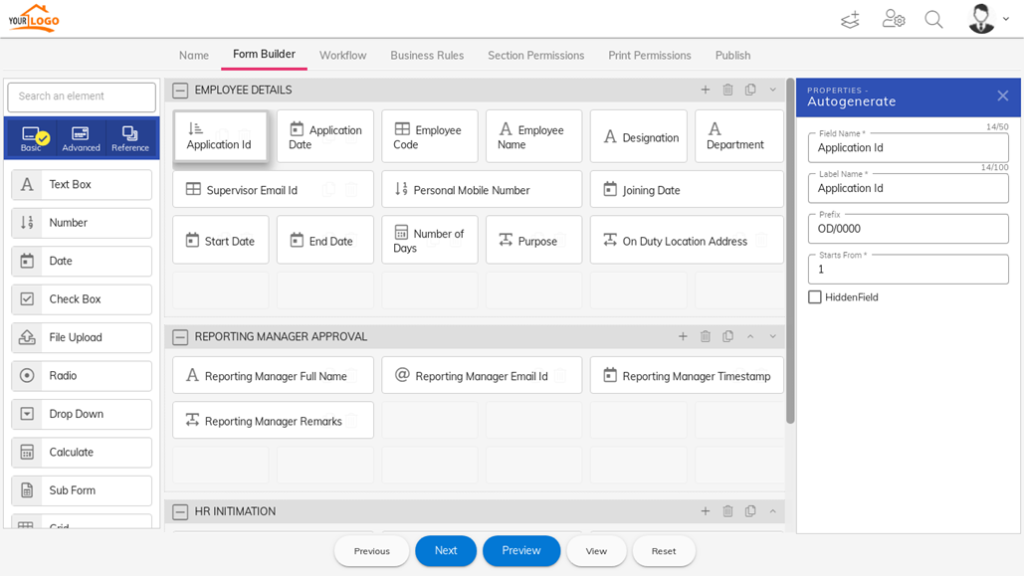
Also read: How to Implement and Govern Citizen Development
By creating a visual and intuitive interface, which graphically replaces the lines of code behind it, end users can set up their application, connect it with databases or web services, integrate it with other tools, and start using it for tackling work tasks. As you can see, app creation and deployment time are drastically reduced.
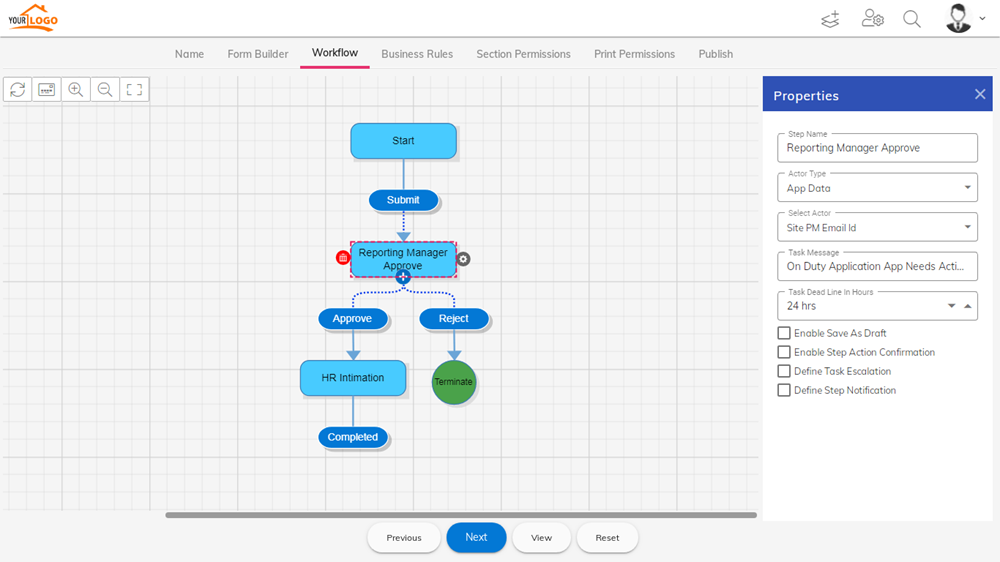
A significant deficit of 85.2 million IT workers is expected by 2030
]
]
]
Who Can Be A Citizen Developer?
Anyone can be a citizen developer, regardless of their technical background or coding experience. The concept of citizen development is to empower non-technical individuals to create their own software applications and technology solutions using low-code and no-code platforms. These platforms are designed to make application development accessible and easy to use, allowing anyone with an idea and the willingness to learn to create their own technology solutions. With the increasing availability of these tools and resources, there is no limit to who can become a citizen developer and create custom applications to solve real-world problems.
Anyone interested in creating software applications or automating business processes can become a citizen developer in an organization. This could include employees from different departments, such as marketing, sales, human resources, or finance, who understand their business processes and the challenges they face. They can leverage low-code and no-code development platforms to create custom applications and automate tasks to increase efficiency and productivity.
Also Read: Meet the Top Citizen Development Influencers
IT professionals and developers can also become citizen developers and use these platforms to create rapid prototypes and proofs-of-concept for testing new ideas and solutions. This can help bridge the gap between business requirements and IT implementation and accelerate development.
Anyone willing to learn and desire to improve their organization’s processes and operations can become a citizen developer and contribute to their organization’s digital transformation.
How to become a Citizen Developer within an Organization?
Here’s the step-by-step guide to becoming a citizen developer within an organization presented in a table format for clarity:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1. Understand the Role | – Definition: A non-technical employee using low-code/no-code platforms to create apps or automate processes. – Purpose: Solve business problems, improve workflows, or enhance productivity. |
| 2. Identify Business Problems | – Observe inefficiencies or repetitive tasks. – Collaborate with colleagues to identify pain points. – Start with small, manageable projects. |
| 3. Learn About Low-Code/No-Code Platforms | – Familiarize yourself with tools – Explore tutorials, documentation, and online courses. |
| 4. Gain Basic Technical Skills | – Learn basic concepts like data structures, workflows, and UI design. – Understand data integration (e.g., spreadsheets, databases, APIs). – Familiarize yourself with basic logic and automation principles. |
| 5. Seek Training and Resources | – Take advantage of organizational training programs. – Enroll in online courses or certifications (e.g., Microsoft Learn for Power Apps). – Join internal communities or forums. |
| 6. Collaborate with IT and Professional Developers | – Work with IT to ensure compliance with policies, security, and governance. – Seek guidance for complex aspects of projects. – Use professional expertise to scale or refine solutions. |
| 7. Start Building Small Projects | – Begin with simple applications or automations (e.g., data collection forms, approval workflows, or dashboards). – Use pre-built templates and drag-and-drop features. |
| 8. Test and Iterate | – Share prototypes with colleagues for feedback. – Test thoroughly to ensure functionality and user needs are met. – Continuously improve based on feedback. |
| 9. Showcase Your Work | – Demonstrate the value of your projects to stakeholders and leadership. – Highlight time savings, cost reductions, or efficiency improvements. – Use success stories to advocate for citizen development. |
| 10. Stay Curious and Keep Learning | – Stay updated on new features and updates to your chosen platforms. – Explore advanced capabilities like AI integration or external system connections. – Network with other citizen developers. |
| 11. Advocate for a Citizen Developer Program | – Propose the creation of a citizen developer program if one doesn’t exist. – Suggest guidelines, training, and governance frameworks to support and scale efforts. |
Why investing in Citizen Developers is beneficial for companies?
The rise of the Citizen Developer movement is changing the way companies approach software development.
According to Gartner, by 2025, 70% of new applications developed by organizations will use low-code or no-code technologies.
“Research indicates that nearly 80% of top-performing companies (pacesetters) in the US utilize citizen developers.”
With low-code and no-code platforms, business professionals can create custom solutions without relying on traditional IT departments. This shift has significant implications for companies and provides numerous benefits that make investing in Citizen Developers a smart choice.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Using low-code and no-code platforms, Citizen Developers can create solutions faster and at a lower cost than traditional software development methods. This makes it easier for companies to stay within budget and get more value for their investment.
Increased Agility
Citizen Developers can respond quickly to changing business needs, delivering solutions in a fraction of the time it would take traditional software development methods. This increased agility allows companies to stay ahead of the competition and quickly pivot to meet new challenges.
Better User Experience
Citizen Developers have a unique perspective on end-users’ needs, allowing them to create tailored solutions to meet their specific needs. This results in a better user experience and increased adoption of the solutions.
Improved Innovation
By empowering Citizen Developers, companies can tap into a new pool of ideas and creativity. This results in increased innovation and the development of unique solutions that can drive growth and competitiveness.
Better Alignment with Business Goals
Citizen Developers have a deep understanding of the business & its goals, allowing them to create solutions that are aligned with the company’s objectives. This results in better outcomes and more efficient use of resources.
The rise of the Citizen Developer movement is a game-changer for companies of all sizes and represents a new era in software development. Within this landscape, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Return on Investment (ROI) serve as the compass guiding organizations toward success. KPIs provide a quantifiable way to evaluate the effectiveness of these initiatives, shedding light on their ability to streamline processes and improve outcomes.
Meanwhile, ROI offers a financial perspective, illuminating the tangible benefits gained from embracing Citizen Development. By understanding and harnessing the potential of Citizen Development KPIs and ROI, businesses can navigate their digital journey with clarity and confidence, driving innovation and growth.

Unleashing the Potential of Citizen Developers Across Industries
The force of citizen developers has taken hold in various industries, including:
- Healthcare: Citizen Developers in healthcare sector are creating No-code apps for patient management, electronic health records, and appointment scheduling.
- Finance: Citizen Developers in Financial institutions use no-code apps for loan origination, fraud detection, and compliance management.
- Marketing and Sales: Teams can streamline their campaign creation and distribution besides using no-code apps for lead management, customer relationship management, etc.
- Retail: Citizen Developers in Retail companies are creating no-code apps for inventory management, customer relationship management, and supply chain management.
- Government: Citizen Developers in Government offices building no-code apps for citizen engagement, service delivery, data management and workflow automation.
- Manufacturing: Citizen Developers in Manufacturing companies are creating no-code apps for production management, quality control, and supply chain management.
- Education: No-code apps are being used in education by Citizen Developers for student management, online learning platforms, and course administration.
- Human Resources: No-code apps are used for recruitment, employee management, and performance evaluation by Citizen Developers in HR departments.
- Telecommunications: Citizen Developers in Telecom companies use no-code apps for network management, customer service, and billing systems.
These are just a few examples of how different industries are already using no-code apps, but they are also being adopted in many other industries.
Also read: Everything you should know about no-code development
What are the Best Practices for Citizen Developers?
- Understand Policies & Governance: Collaborate with IT, follow organizational guidelines, and seek approvals to ensure compliance with security and governance standards.
- Start Small & Focus on Value: Identify pain points, deliver quick wins, and avoid overcomplicating initial projects.
- Leverage Low-Code/No-Code Tools: Choose the right platform, use pre-built templates, and learn the basics of the tool.
- Prioritize User Experience (UX): Design for end users, gather feedback, and test thoroughly before deployment.
- Ensure Data Security & Compliance: Protect sensitive data, follow governance rules, and monitor access to applications.
- Collaborate with IT & Professionals: Seek guidance for complex tasks, leverage professional expertise, and build partnerships.
- Document Your Work: Maintain clear documentation, share knowledge, and track changes.
- Test & Iterate: Test thoroughly, gather feedback, and monitor performance post-deployment.
- Plan for Scalability & Maintenance: Design for growth, plan for updates, and ensure long-term maintenance.
- Stay Within Your Limits: Know when to seek help, avoid overreach, and respect boundaries.
- Continuously Learn & Improve: Stay updated on platform features, expand your skills, and network with other citizen developers.
- Advocate for a Citizen Developer Program: Promote collaboration, share success stories, and build a community of citizen developers.
These best practices ensure citizen developers create effective, secure, and impactful solutions while aligning with organizational goals.
Quixy – An Ideal platform for Citizen Developers
Quixy is a low-code no-code platform that enables users with minimal technical expertise to develop custom business applications and automate processes. It provides an intuitive, drag-and-drop interface for creating custom solutions without writing code. This makes it possible for employees to take ownership of their business challenges and develop solutions to meet their specific needs, empowering them to become citizen developers.
Although there are some characteristics of Citizen developers that can make someone particularly well-suited for the profession, such as a problem-solving mindset and a willingness to learn, anyone can become a citizen developer with the right tools and resources. You can also check out Citizen Developer’s Toolbox: Insights and Strategies from Our eBook-Innovate and Empower: A Journey through Citizen Development!
With Quixy, users can quickly design, test, and deploy business applications that fit their unique requirements, reducing the dependence on IT professionals and streamlining the development process. Additionally, its features, such as integration with existing systems and collaboration tools, facilitate seamless teamwork and faster problem-solving. The citizen development value tree can act as a universal language, bringing teams together and harmonizing collaboration for project success.
Quixy empowers you to create your own apps by providing a low-code platform that enables you to create custom business solutions, automate processes, and streamline collaboration without requiring extensive technical skills. And helping citizen developers across verticals build applications in days and weeks to automate their manual processes and drive efficiency, productivity, and transparency. Don’t miss out on the chance to elevate your processes. Take the first step and get started with Quixy today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some of the frequently asked questions related to the rise of citizen developers and why businesses should care:
Q: Who is a citizen developer?
A: A citizen developer is a non-professional developer who creates applications or tools using low-code or no-code development platforms. They are typically business users or employees with a strong understanding of the company’s operations and needs.
Q: Why is there a rise in citizen developers?
A: The rise of citizen developers is driven by the increasing demand for customized and flexible solutions, as well as the availability of user-friendly low-code and no-code development platforms that enable non-technical users to create applications and tools.
Q: Why do businesses need citizen developers?
A: We need citizen developers for several reasons:
Accelerated development: Citizen developers can help businesses accelerate the development process by creating applications and tools without relying on IT departments. This can help businesses bring new products and services to market faster and respond quickly to changing business needs.
Customized solutions: Citizen developers are business users who have a deep understanding of the company’s operations and needs. By allowing them to create their own applications, businesses can get customized solutions that meet their specific requirements.
Cost savings: Citizen development can help businesses reduce the cost of development by using low-code or no-code platforms that don’t require specialized technical skills.
Innovation and collaboration: Citizen development fosters a culture of innovation and collaboration within the organization. By empowering employees to create their own applications, businesses can tap into the creativity and ingenuity of their workforce.
Citizen development can help businesses become more agile, innovative, and efficient by enabling non-technical users to create their own applications and tools.
Q: What are the most popular tools that citizen developers use?
A: The most popular tools that citizen developers use are low-code or no-code development platforms. These platforms provide a user-friendly interface and pre-built components that allow non-technical users to create applications and tools without writing code. One of the most popular no-code platform is Quixy, platform provides a range of pre-built templates, components, and integrations that can help citizen developers quickly create applications and tools that meet their business needs.
Q: How can businesses empower citizen developers?
A: To empower citizen developers, businesses can take the following steps:
Provide training and resources: Citizen developers may not have formal training in software development, so it’s important to provide them with the training and resources they need to be successful. This could include online courses, documentation, and mentorship programs.
Establish clear guidelines and governance frameworks: To ensure that citizen-developed applications are secure, compliant, and aligned with the organization’s objectives, businesses should establish clear guidelines and governance frameworks for development projects.
Foster a culture of innovation and collaboration: Citizen development works best when there is a culture of innovation and collaboration within the organization. Businesses can encourage this culture by recognizing and rewarding innovative ideas and providing opportunities for cross-functional collaboration.
Provide access to low-code or no-code development platforms: Citizen developers need access to low-code or no-code development platforms to be able to create applications and tools. Businesses can provide access to these platforms through internal IT teams or by using cloud-based platforms.
Encourage feedback and input from IT teams: While citizen developers can create applications and tools on their own, it’s important to involve IT teams in the process to ensure compliance with security and data privacy regulations. Businesses should encourage citizen developers to seek input and feedback from IT teams throughout the development process.
By taking these steps, businesses can empower citizen developers to create customized solutions that meet their unique needs and accelerate the development process. Additionally, empowering citizen developers can help foster a culture of innovation and collaboration within the organization.
Q. Can I be a Citizen Developer?
Yes, you can be a citizen developer. Citizen development refers to the practice of creating software applications, websites, and other technology solutions by people who are not professional developers. With the increasing availability of low-code and no-code development platforms, it has become easier for individuals with no coding experience to build their own applications.
Discover the step-by-step guide on how to become a citizen developer and create your own technology solutions by checking out our latest blog post!
Subscribe
Login
Please login to comment
0 Comments
Oldest